Jenkins
Using the CLI in a CI/CD pipeline
We’ve optimized the Checkly CLI to work in any CI/CD workflow. Here are the basics you need to know that will come in handy when adapting the examples we give you to your own, specific setup.
- For authentication, make sure to set the
CHECKLY_API_KEYandCHECKLY_ACCOUNT_IDparameters as environment variables in your CI/CD platform. - Set the reporter you want to use for the
testcommand using the--reporterflag, i.e.--reporter=dot. - To store a test session with full logging, traces and vides, set the
--recordflag for thetestcommand. - Use the
--forceflag on thedeployand / ordestroycommands to skip the normal confirmation steps.
When using the --record flag, the CLI will attempt to parse git specific information from
the environment to display in the recorded test session as metadata. However, you can also set these data items specifically
by using environment variables.
| item | auto | variable | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repository | false | repoUrl in checkly.config.ts or CHECKLY_REPO_URL |
The URL of your repo on GitHub, GitLab etc. |
| Commit hash | true | CHECKLY_REPO_SHA |
The SHA of the commit. |
| Branch | true | CHECKLY_REPO_BRANCH |
The branch name. |
| Commit owner | true | CHECKLY_REPO_COMMIT_OWNER |
The committer’s name or email. |
| Commit message | true | CHECKLY_REPO_COMMIT_MESSAGE |
The commit message. |
| Environment | false | CHECKLY_TEST_ENVIRONMENT |
The environment name, e.g. “staging” |
Check the CLI command line reference for more options.
Configuring Jenkins to run the Checkly CLI
As the Checkly CLI is a Node.js project, the main step you need to take is install the NodeJS plugin.
- In Jenkins, go to Manage Jenkins → Plugins → Available plugins and look for the NodeJS plugin and install it.
- After installing the NodeJS plugin, we need to configure it. Head over to Manage Jenkins → Tools and click “Add NodeJS”
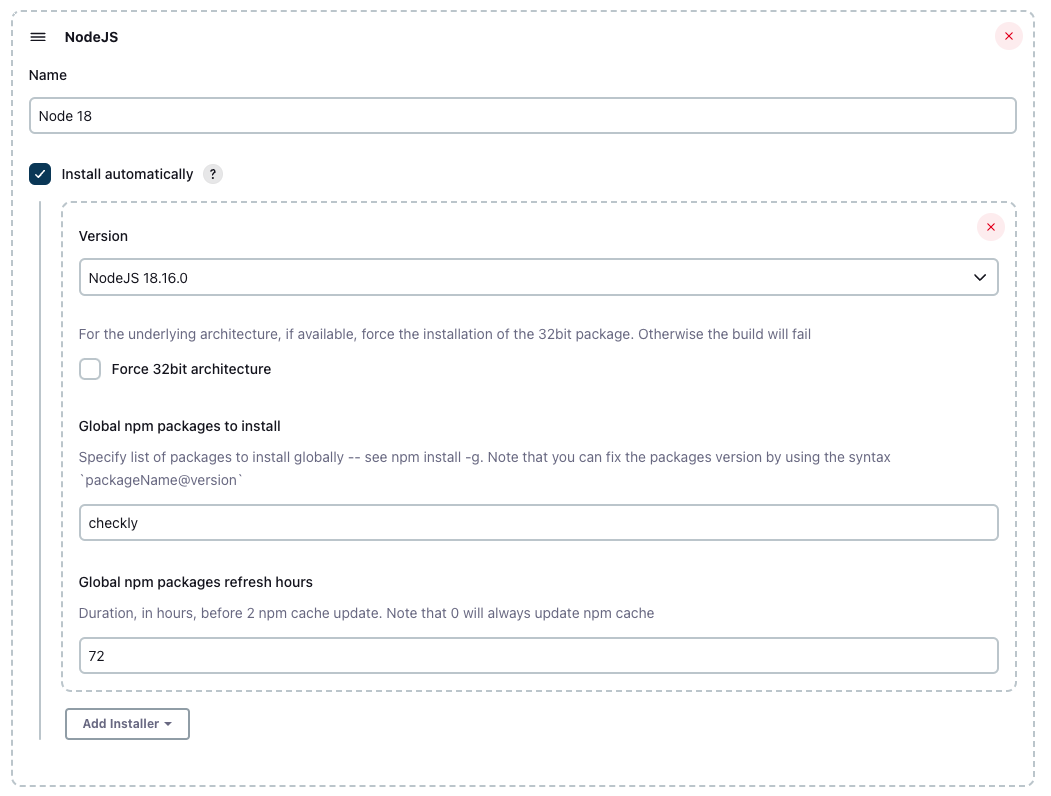
We recommend using any Node.js stable version higher than 16.x.
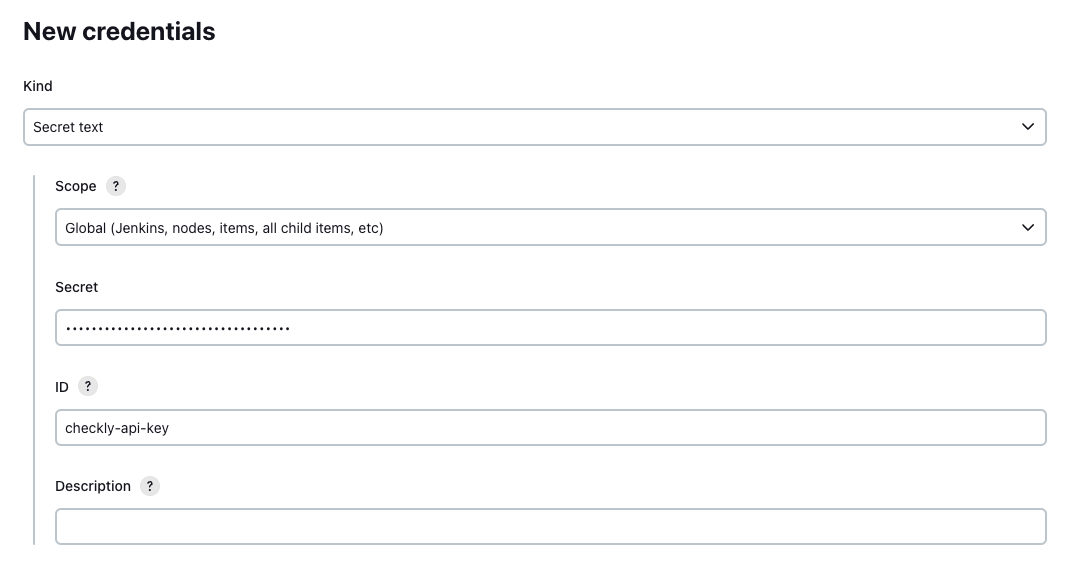
Set your Checkly credentials
Navigate to Manage Jenkins → Manage Credentials to add your Checkly account ID and API key to your preferred scope. Store them as “secret text” and assign and ID to the credential.
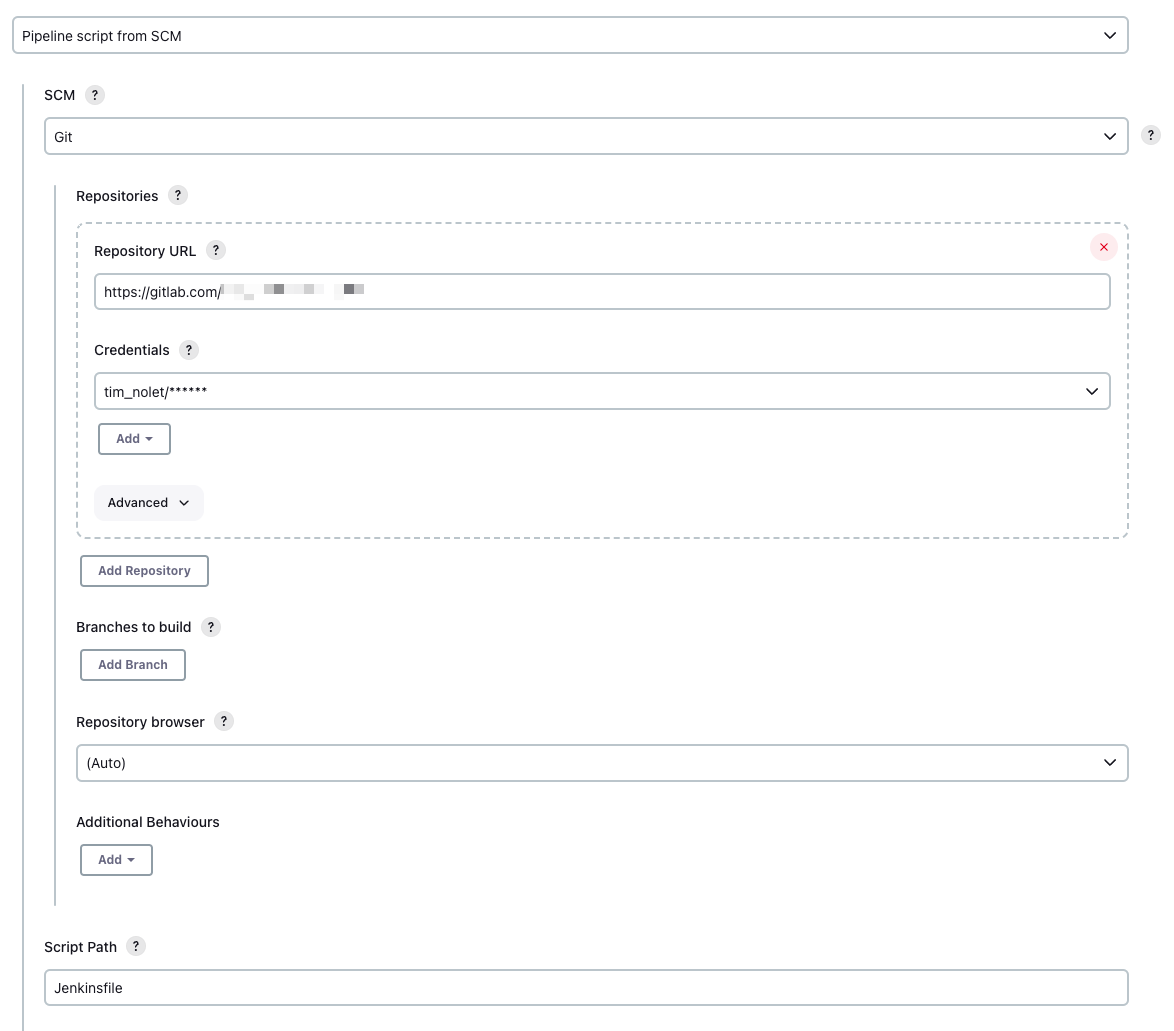
Configuring the Jenkins Pipeline
Add the Jenkinsfile to your repo that defines the basic stages and steps. Make sure to set up your SCM settings
correctly so Jenkins can fetch your git repo and look for the Jenkinsfile in the root of your project.
The actual contents of your Jenkinsfile will differ based on your code and how you deploy. But in general, your pipeline
should look as follows:
- You deploy your application first.
- You install the required dependencies for the Checkly CLI.
- You run the
checkly testcommand.
// Jenkinsfile
pipeline {
agent any
tools {nodejs "Node 18"}
environment {
CHECKLY_API_KEY = credentials('checkly-api-key')
CHECKLY_ACCOUNT_ID = credentials('checkly-account-id')
CHECKLY_TEST_ENVIRONMENT='production'
}
stages {
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Deploying....'
}
}
stage('Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm ci'
}
}
stage('checkly test') {
steps {
sh 'npx checkly test --record'
}
}
stage('checkly deploy') {
when {
branch "main"
}
steps {
sh 'npx checkly deploy --force'
}
}
}
}
Last updated on April 25, 2024. You can contribute to this documentation by editing this page on Github